EKS Auto Mode
Table of Contents
Overview #
Amazon EKS Auto Mode is a fully managed Kubernetes infrastructure automation feature that simplifies the deployment and operation of EKS clusters. It allows AWS to manage not just the Kubernetes control plane, but also the underlying infrastructure, including compute, networking, and storage.
Key Features #
-
Fully Automated Infrastructure: AWS provisions and manages compute, networking, and storage resources.
-
Dynamic Scaling: Automatically adds/removes nodes based on workload demands using Karpenter.
-
Security Best Practices:
-
Immutable AMIs with SELinux and read-only root filesystems.
-
Nodes are automatically recycled every 21 days (or less).
-
Integrated Add-ons: Core Kubernetes components like DNS, load balancing, and storage are managed as built-in features:
When upgrading the EKS version, one of the most time-consuming tasks for our team is planning and upgrading the associated components. With EKS in auto mode, these are now built-in add-on features, so we no longer need to manage them manually.
| Add-on | Before | with Auto Mode |
|---|---|---|
| kube-proxy | Managed by user | Managed by AWS |
| coredns | Managed by user | Managed by AWS |
| vpc-cni | Managed by user | Managed by AWS |
| aws-load-balancer-controller | Managed by user | Managed by AWS |
| Karpenter | Managed by user | Managed by AWS |
| Storage csi | Managed by user | Managed by AWS |
| cluster-auto-scaler | Managed by user | Not required, replaced by Karpenter |
Enabling auto mode on Existing Cluster #
1. Prerequisites #
Before using Amazon EKS Auto Mode, ensure the following.
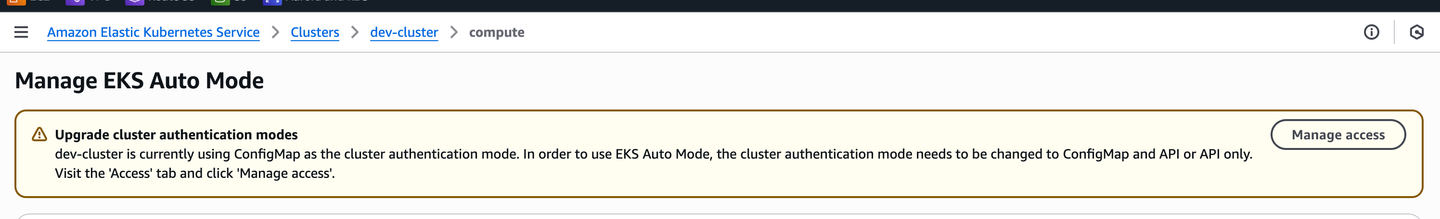
1.1 Access Entries #
To enable Amazon EKS Auto Mode, you must use the API or API_AND_CONFIG_MAP cluster authentication modes.
1.2 Cluster IAM role #
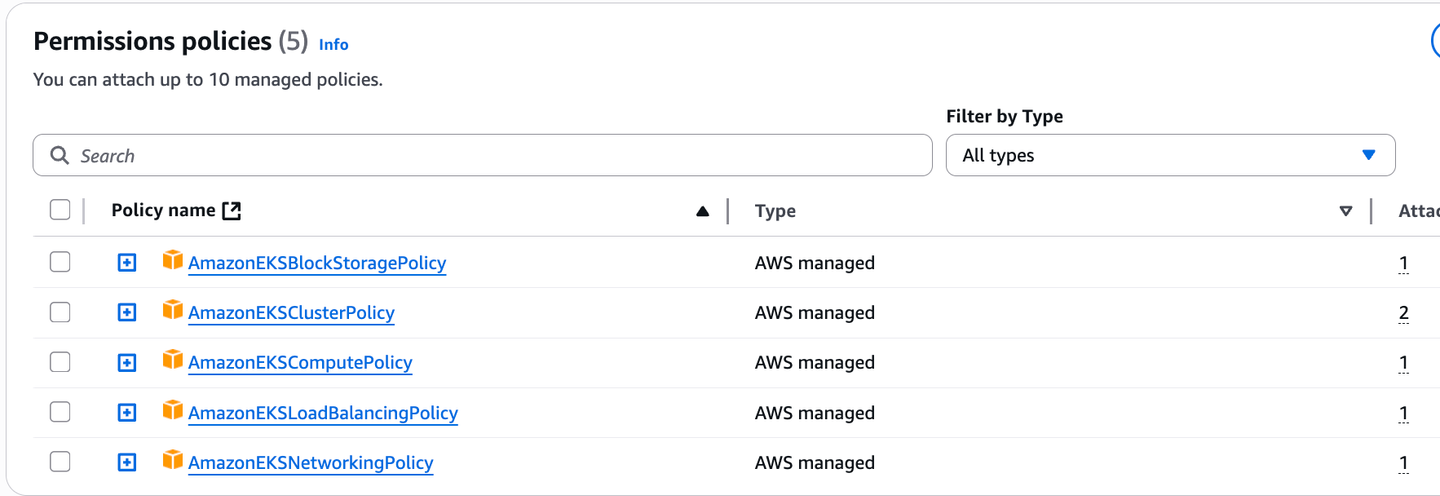
Cluster IAM role of an EKS Cluster cannot be changed after the cluster is created. EKS Auto Mode requires additional permissions on this role. You must attach additional policies to the current role.
- Navigate to Cluster IAM role and adding the following policies
- AmazonEKSComputePolicy
- AmazonEKSBlockStoragePolicy
- AmazonEKSLoadBalancingPolicy
- AmazonEKSNetworkingPolicy
- AmazonEKSClusterPolicy ( already exist )
- Edit the trust Policy and add sts:TagSession to allow Action.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "eks.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": [
"sts:AssumeRole",
"sts:TagSession"
]
}
]
}
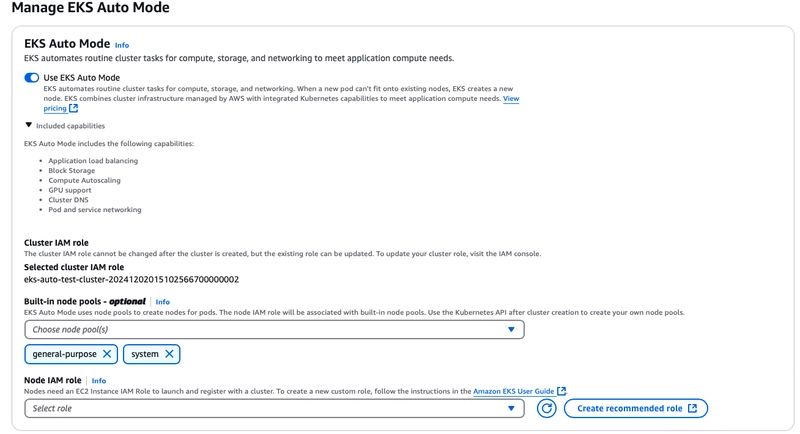
1.3 Node IAM role #
EKS auto uses Karpenter behind the scenes for scaling, and it requires a node IAM role to manage EC2-related actions.
NOTE: Karpenter, a node provisioning tool that helps optimize cluster scaling and resource utilization. With Karpenter’s NodePool resource, you can define specific requirements for your compute resources, including instance types, availability zones, architectures, and capacity types.
You can either select Create recommended roles for the Node IAM Role, or create the IAM role separately.
1.4 Terraform support #
Terraform support for EKS Auto Mode was introduced in AWS provider version v5.79.0. Community EKS terraform module support for Auto Mode was added in version 20.31.0. Please ensure you’re using at least these versions.
2. Enable Auto Mode on Cluser #
Follow steps document in: Enable EKS Auto Mode on an existing cluster - Amazon EKS
3. Migrate from EKS Managed Node Groups to EKS Auto Mode #
Follow steps document in: Migrate from EKS Managed Node Groups to EKS Auto Mode - Amazon EKS
4. Migrate from Karpenter to EKS Auto Mode using kubectl #
Follow steps document in: Migrate from Karpenter to EKS Auto Mode using kubectl - Amazon EKS
EKS Auto Mode vs Fargate #
AWS Fargate is a serverless compute engine for containers that eliminates the need to provision and manage worker nodes. Below is a comparison between the two:
| Feature | EKS Auto Mode | Fargate |
|---|---|---|
| Worker Nodes | Karpenter managed instances | Serverless; one pod per vm |
| Core Add-ons | Managed by AWS | Managed by user |
| EC2 Instance Types | All | Non GPU |
| DaemonSets | ✅ | ❌ |
| Stateful Apps | ✅ | ❌ |
| Networking | Supports public and private subnets. | Limited to private subnets. |
| Load Balancers | Compatible with Classic (CLB), Network (NLB), and Ingress. | Only Ingress-supported. |
| Custom Networking | ✅ | ❌ |
According to the AWS documentation, it appears that AWS is recommending customers to use EKS Auto Mode over Fargate:
Amazon EKS with AWS Fargate remains an option for customers who want to run EKS, but Amazon EKS Auto Mode is the recommended approach moving forward
Enabling auto mode on new Cluster #
See eks module for more examle. terraform-aws-eks/examples/eks-auto-mode/main.tf at master · terraform-aws-modules/terraform-aws-eks
################################################################################
# EKS Module
################################################################################
module "eks" {
source = "terraform-aws-modules/eks/aws"
version = "~> 20.31"
cluster_name = local.name
cluster_version = local.cluster_version
cluster_endpoint_public_access = false
enable_cluster_creator_admin_permissions = true
cluster_compute_config = {
enabled = true
node_pools = ["general-purpose"]
}
vpc_id = module.vpc.vpc_id
subnet_ids = module.vpc.private_subnets
tags = local.tags
}
EKS Auto Mode pricing #
EKS Auto Mode includes a management fee that varies depending on the EC2 instance type launched, in addition to the standard EC2 instance costs. For more details, see the EKS pricing page: Amazon EKS Pricing | Managed Kubernetes Service | Amazon Web Services